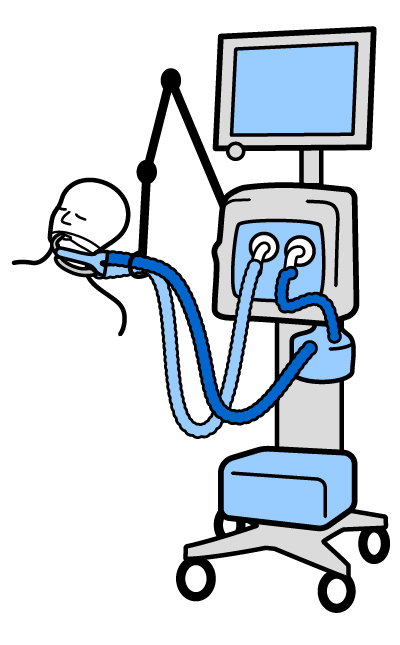
A ventilator is a machine to support breathing. It pushes air and oxygen into the lungs and removes carbon dioxide. Children can be on a ventilator due to:
A child is connected to the ventilator through a breathing tube. One type of tube goes through the mouth or the nose to the lungs. This is called an endotracheal tube (ETT).
Another type of tube goes directly into the windpipe. It is called a tracheostomy tube. Some people call it a “trachy” for short.
This topic was reviewed by a paediatric intensive care specialist in July 2022.